PRODUCTS & RD
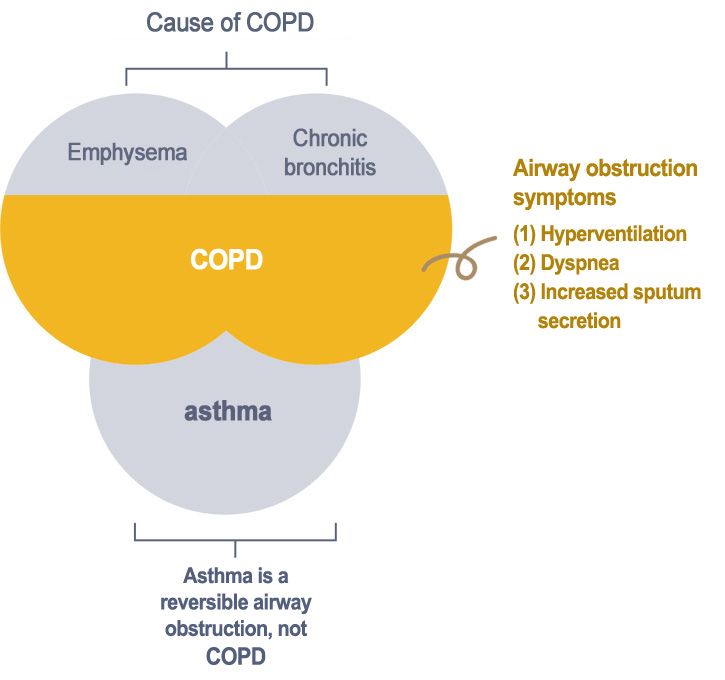
Definition of COPD by American Thoracic Society, ATS
COPD cannot be cured and will cause permanent lung damage in patients. Increased risk for IPF has been associated with several environmental exposures, such as airborne particles and toxic substances. Long term exposure to these risk factors leads to persistent chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract, which in turn damage the alveoli and makes them separated from the small respiratory tract. In addition, exacerbating inflammation, increased oxidative pressure and dysregulation of protease will promote mucosal swelling and pulmonary fibrosis. The structural change will disrupt the airflow and eventually damage the lung function. The main purpose of current treatments for COPD are: (1) to relieve the symptoms of patients, such as improving life quality and increasing exercise tolerance (2) to slow down decline in lung function.
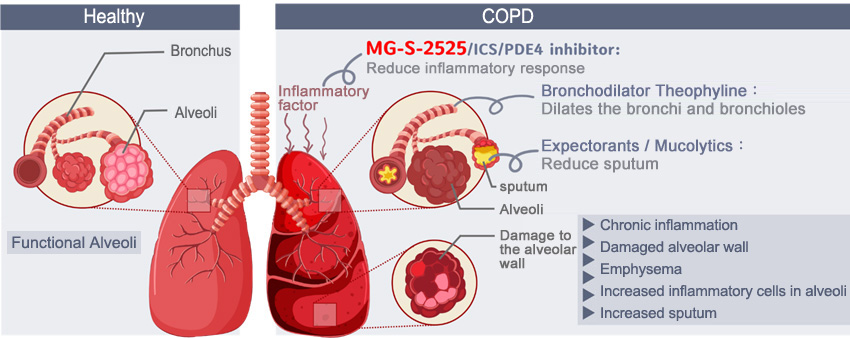
MG-S-2525 first in class drug for COPD
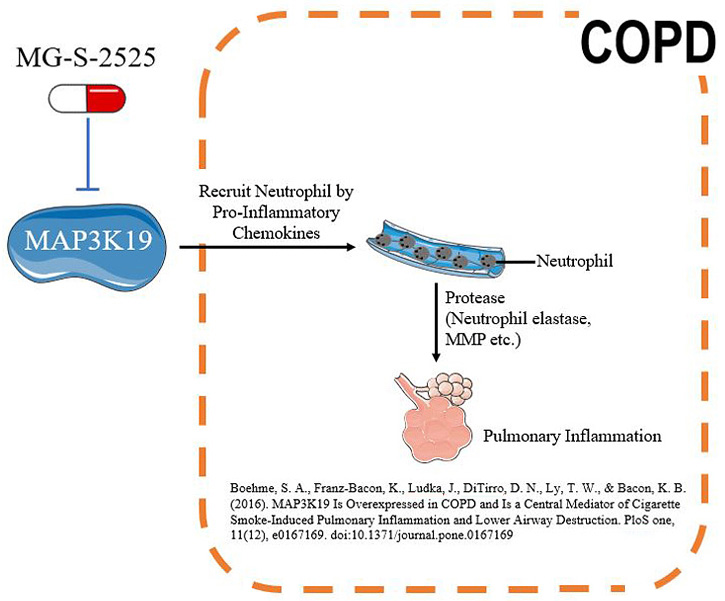
MG-S-2525 mechanism in COPD
COPD drugs are currently mainly divided into inhaled drugs and oral drugs. Inhaled drugs are mainly bronchodilators and steroids; oral drugs include steroids, theophylline, and type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4) inhibitors, (Roflumilast, AstraZeneca), antibiotics and expectorants/mucolytics. The role of MG-S-2525 in treating COPD is similar to that of Roflumilast, which has sales of approximately US$215 million in 2019.
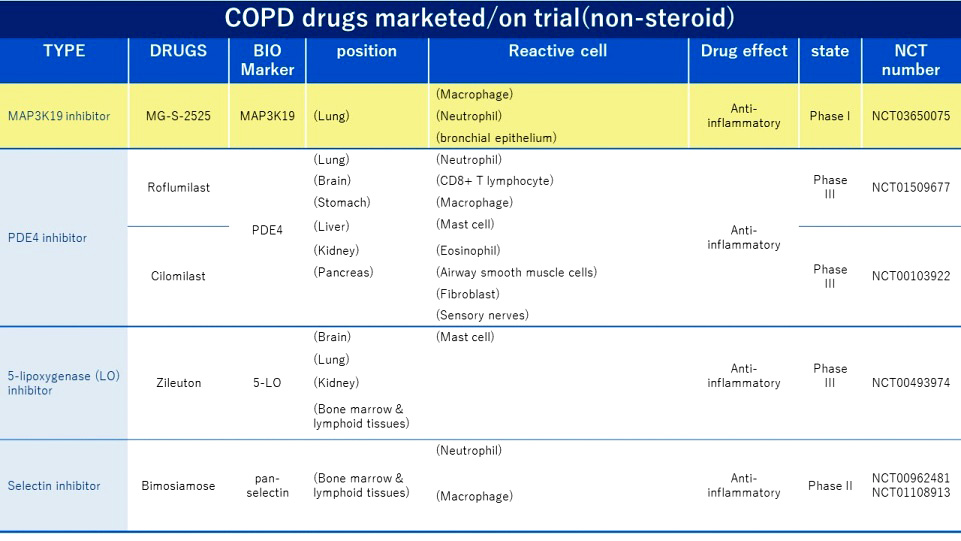
COPD drugs marketed/ on-going(Non-Steroid)
The small molecule first-in-class drug MG-S-2525 from Metagone Biotechnology’s can effectively inhibit the signal transduction of the novel protein kinase MAP3K19. Researches have shown that the decreased expression or activity of MAP3K19 in lung tissue result in a reduction of pneumonia inflammation. The advantages of MG-S-2525 are as follows: (1) Limited side effects: The target is located specifically in the lungs, which reduce the drug's impact on other organs. (2) High safety dose: the dose can reach 800 mg and the safety is good. (3) Anti-inflammatory effect. Currently, MG-S-2525 (First in class) has been approved of human clinical trial review (IND) and the first phase of human clinical trials by the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) and the Food and Drug Administration of the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare (TFDA) on July 25, 2018 and November 16, 2018, respectively. The Phase I trial was completed in August 2019, confirming that MG-S-2525 does not cause adverse reactions in humans. The Phase II trial will be conducted in Q1 2021, and Phase IIa is expected to be completed in Q3 2021.